How iCAGES works
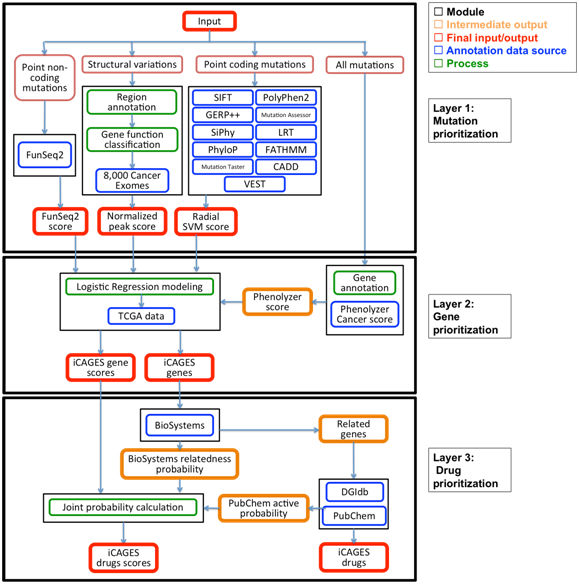
A flowchart to show the process of iCAGES package. The iCAGES package consists of three layers. The input file contains all variants identified from the patient; it can be either in ANNOVAR input format or in VCF format. The first layer of iCAGES prioritizes mutations. It computes three different feature scores for annotating the gene, including radial SVM score for each of its point coding mutation, CNV normalized peak score for each of its structural variation and FunSeq2 score for each of its point non-coding mutation. The second layer of iCAGES prioritizes cancer driver genes. It takes three features scores from the first layer, generates the corresponding Phenolyzer score for each mutated gene and computes an LR score for this gene (iCAGES gene score). The final level of iCAGES prioritizes targeted drugs. It first queries DGIdb for potential drugs that interact with the patient’ s mutated genes and their neighbors. Next, it calculates the joint probability for each drug being the most effective (iCAGES drug score) from three feature scores, which are iCAGES score for its direct/indirect target, normalized BioSystems probability measuring the maximum relatedness of the drugs’ direct target with each mutated gene (final target) in the patient and PubChem active probability measuring the bioactivity of the drug. The final output of iCAGES consists of three major elements, a prioritized list of mutations, a prioritized list of genes with their iCAGES gene scores as well as a prioritized list of targeted drugs with their iCAGES drug scores, all highlighted in red.